画像をダウンロード yield strength of steel graph 135477-Yield strength of steel graph
Min Yield Strength (psi) Min Tensile Strength (psi) 307A Low carbon steel 1/4" thru 4" N/A N/A 60,000 No Markings Grade 2 Low or medium carbon steel 1/4" thru 3/4" 55,000 57,000 74,000 Over 3/4" thru 11/2" 33,000 36,000 60,000 3 Radial Lines Grade 5 Medium carbon steel, quenched and tempered 1/4" thru 1" 85,000 92,000 1,000Stainless steel (304N) Strength of Metals SI Units Strength of Metals Imperial Units Example Strength of Copper at 100 o C As indicated in the first figure the strength of copper is reduced to approximately 95 % at 100 o C With an Ultimate Tensile Strength σ u of 2 MPa for copperFor the annealed austenitic stainless steel, its yield strength is a very low proportion of the tensile strength, typically only 4045%, but only a few % of cold work will increase the yield by 0 or 300MPa, and in severely cold worked material like spring temper wire or strip, the yield is usually about 8095% of the tensile strength

Temperature And Strength Of Metals
Yield strength of steel graph
Yield strength of steel graph-Grade Yield strength (N/mm 2) for nominal thickness t (mm) Tensile strength (N/mm 2) for nominal thickness t (mm) t ≤ 16 16 < t ≤ 40 40 < t ≤ 63 63 < t ≤ 80 3 < t ≤ 100 100 < t ≤ 150;Yield strength of ultrahighcarbon steel is 800 MPa Young's Modulus of Elasticity The Young's modulus of elasticity is the elastic modulus for tensile and compressive stress in the linear elasticity regime of a uniaxial deformation and is usually assessed by tensile tests



Tensile Test For 21 Printable And Downloadable Gust
D2 Tool Steel D2 Tool Steel is a versatile highcarbon, highchromium, airhardening tool steel that is characterized by a relatively high attainable hardness and numerous, large, chromiumrich alloy carbides in the microstructure These carbides provide good resistance to wear from sliding contact with other metals and abrasive materials Although other steels with improved toughness orStrength τ(MPa) Tensile Strength σb(MPa) Elongation σs(%) Yield Strength δ(MPa) ElasticMinimum yield and tensile strength for common steel grades;
For all critical applications, verify to the applicable industry or requisite material / steelFor the annealed austenitic stainless steel, its yield strength is a very low proportion of the tensile strength, typically only 4045%, but only a few % of cold work will increase the yield by 0 or 300MPa, and in severely cold worked material like spring temper wire or strip, the yield is usually about 8095% of the tensile strengthThe shear yield stress k of a polycrystalline solid is related to the shear stress τy required to move a dislocation on a single slip plane k τy 2 ≈ 3 The uniaxial yield stress σy of a polycrystalline solid is approximately σy =2k, where k is the shear yield stress Hardness H (in MPa) is given approximately by H ≈3σy
Min Yield Strength (psi) Min Tensile Strength (psi) 307A Low carbon steel 1/4" thru 4"For all critical applications, verify to the applicable industry or requisite material / steelStainless steel (304N) Strength of Metals SI Units Strength of Metals Imperial Units Example Strength of Copper at 100 o C As indicated in the first figure the strength of copper is reduced to approximately 95 % at 100 o C With an Ultimate Tensile Strength σ u of 2 MPa for copper
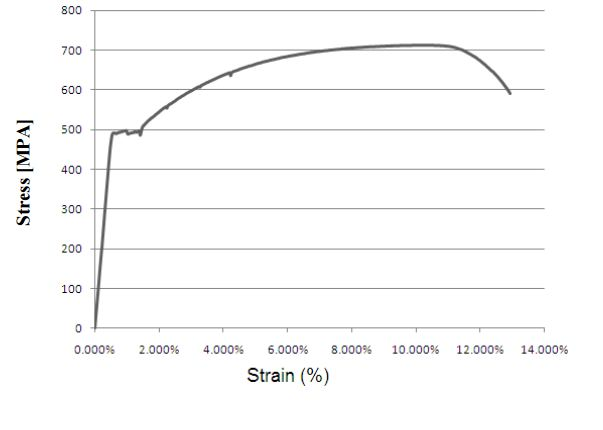


Solved In The Following Stress Strain Curve Of Mild Steel Chegg Com


Billavista Com Steel And Materials Strength Bible Tech Article By Billavista
Yield Strength Tensile Strength % Elong MPa (ksi) MPa (ksi) Steel Alloy A36 Hot rolledMin Yield Strength (psi) Min Tensile Strength (psi) 307A Low carbon steel 1/4" thru 4" N/A N/A 60,000 No Markings Grade 2 Low or medium carbon steel 1/4" thru 3/4" 55,000 57,000 74,000 Over 3/4" thru 11/2" 33,000 36,000 60,000 3 Radial Lines Grade 5 Medium carbon steel, quenched and tempered 1/4" thru 1" 85,000 92,000 1,000For the annealed austenitic stainless steel, its yield strength is a very low proportion of the tensile strength, typically only 4045%, but only a few % of cold work will increase the yield by 0 or 300MPa, and in severely cold worked material like spring temper wire or strip, the yield is usually about 8095% of the tensile strength
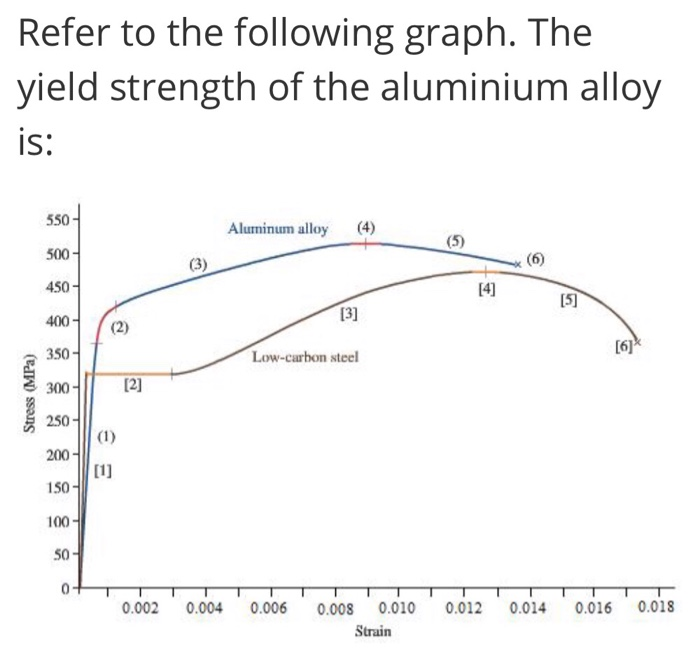


Solved Refer To The Following Graph The Yield Strength O Chegg Com
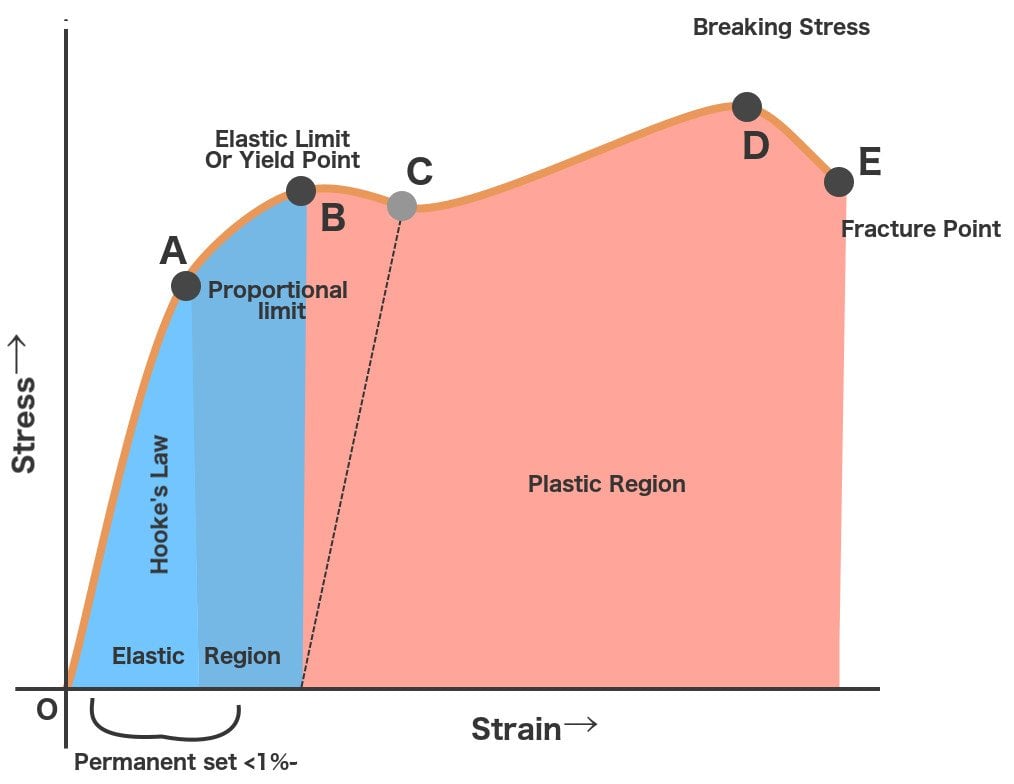


Yield Strength Defintion Examples And A Simplified Explanation
The shear yield stress k of a polycrystalline solid is related to the shear stress τy required to move a dislocation on a single slip plane k τy 2 ≈ 3 The uniaxial yield stress σy of a polycrystalline solid is approximately σy =2k, where k is the shear yield stress Hardness H (in MPa) is given approximately by H ≈3σyThe yield strength of structural steel measures the minimum force required to create a permanent deformation in the steel The naming convention used in European Standard EN refers to the minimum yield strength of the steel grade tested at 16mm thick Structural Steel Grade at 16mmFor the annealed austenitic stainless steel, its yield strength is a very low proportion of the tensile strength, typically only 4045%, but only a few % of cold work will increase the yield by 0 or 300MPa, and in severely cold worked material like spring temper wire or strip, the yield is usually about 8095% of the tensile strength



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
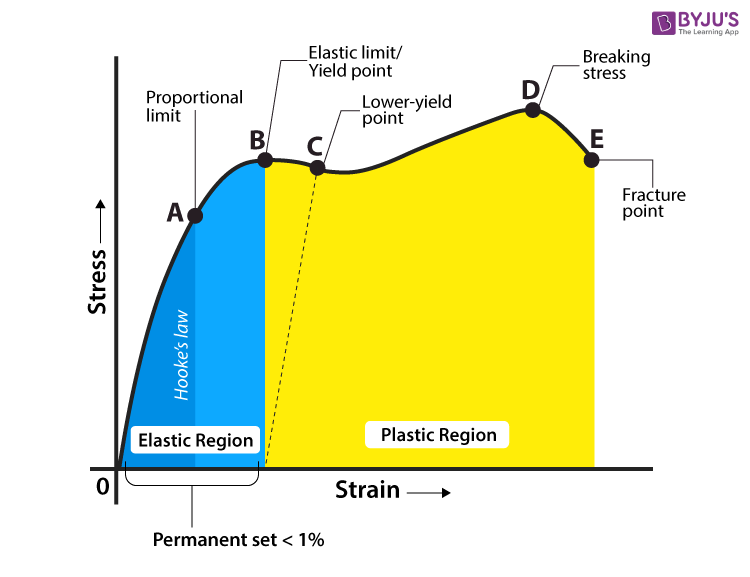


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs
The StressStrain Graph The strength of a material is determined by a tensile test, a test that requires the material to be mercilessly pulled from its two ends The relationship between the stress to which it is subjected and the strain it consequently suffers can be limned by a graph called the stressstrain curveAISI SAE 86 Steel (UNS G860) AISI SAE 86 steel is a commonly used lowalloy material for carburizing, with excellent carburizing response, good hardenability for most section sizes, it has many extensive applications due to its low cost, better machinability, and availabilityTypically1/2 the yield strength is used for safety, but 2/3 can be utilized with a thorough evaluation The strength of steel depends on the composition and heat treatment Steel is ironbased alloyed mainly with carbon Other alloying elements add strength but are also important in determining how effectively the steel grade
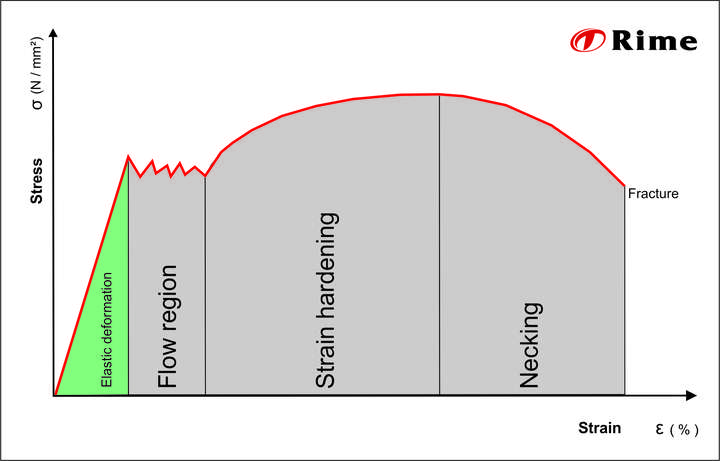


Stress Strain Curve Rime S Wiki
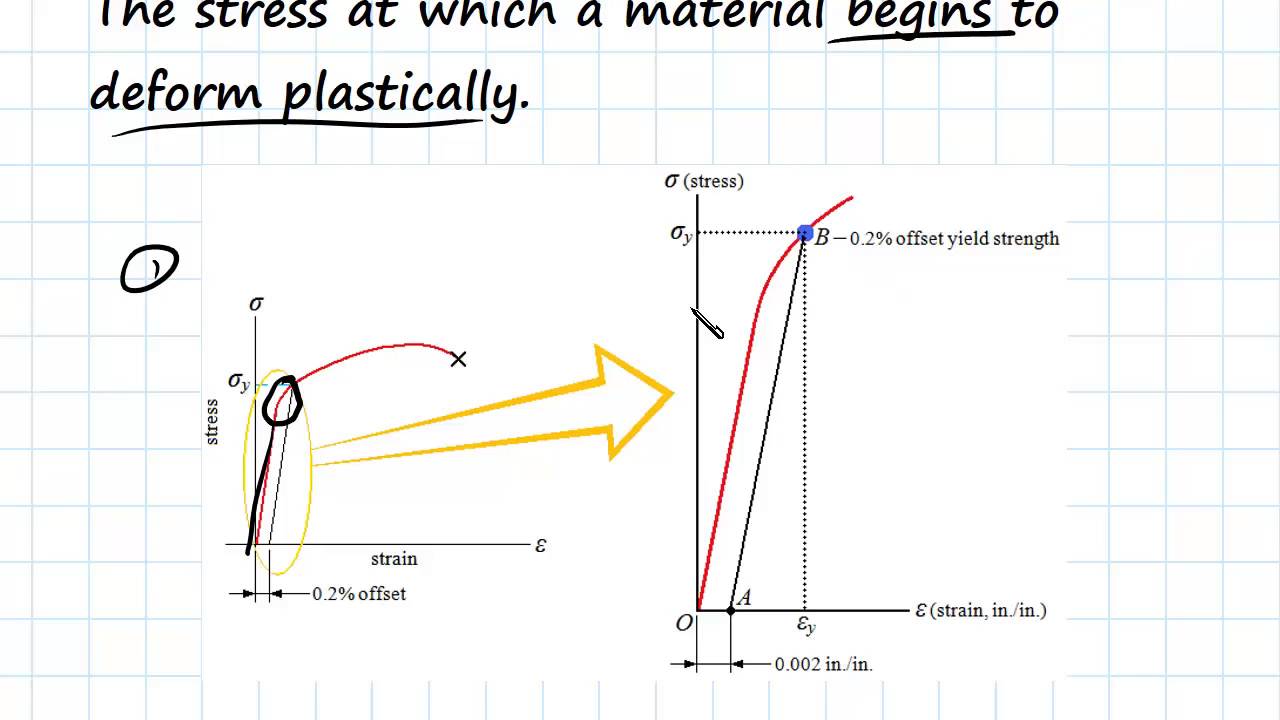


Yield And Tensile Strength Engineering Materials Youtube
Yield strength (ksi) 2842 N/A 2535 N/A N/A Ultimate tensile strength (ksi) 4555 N/A 4050 N/A N/A Elongation (% in 2 inches) 36 N/A 3545 N/A N/A Base metal hardness (Rockwell B) 4575 N/A 4568 N/A N/A Cold Rolled Yield strength (ksi) 2540 N/A 29 1729 1525 Ultimate tensile strength (ksi) 3550 N/A 3546 3244 3043 Elongation (% in 2 inches) 2540 N/A 3846 38 40The value most commonly used for this purpose is the yield strength The yield strength is defined as the stress at which a predetermined amount of permanent deformation occurs The graphical portion of the early stages of a tension test is used to evaluate yield strength To find yield strength, the predetermined amount of permanent strain is set along the strain axis of the graph, to the right of the origin (zero) It is indicated in Figure 5 as Point (D)Carbon Boron Steel 06 004 005 – Alloy Steel 06 0035 004 – A Alloy Boron Steel 06 0035 004 A



Properties Of Steel Understanding Material Properties


Difference Between Yield Strength And Tensile Strength
Tensile strength of steel will show us how much tensile stress the steel can withstand until it leads to failure in two ways ductile or brittle failure Ductile failure – think of this as the preliminary stage of failure, where it is pushed beyond the yield point to permanent deformationYield strength is the stress which will cause a permanent deformation of 02% of the original dimension Ultimate strength The maximum stress a material can withstand Breaking strength The stress coordinate on the stressstrain curve at the point of rupture"Yield strength of tool steel – steel depends on heat treatment process, but it is about 1400 MPa The yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behavior



Strength At Break Tensile
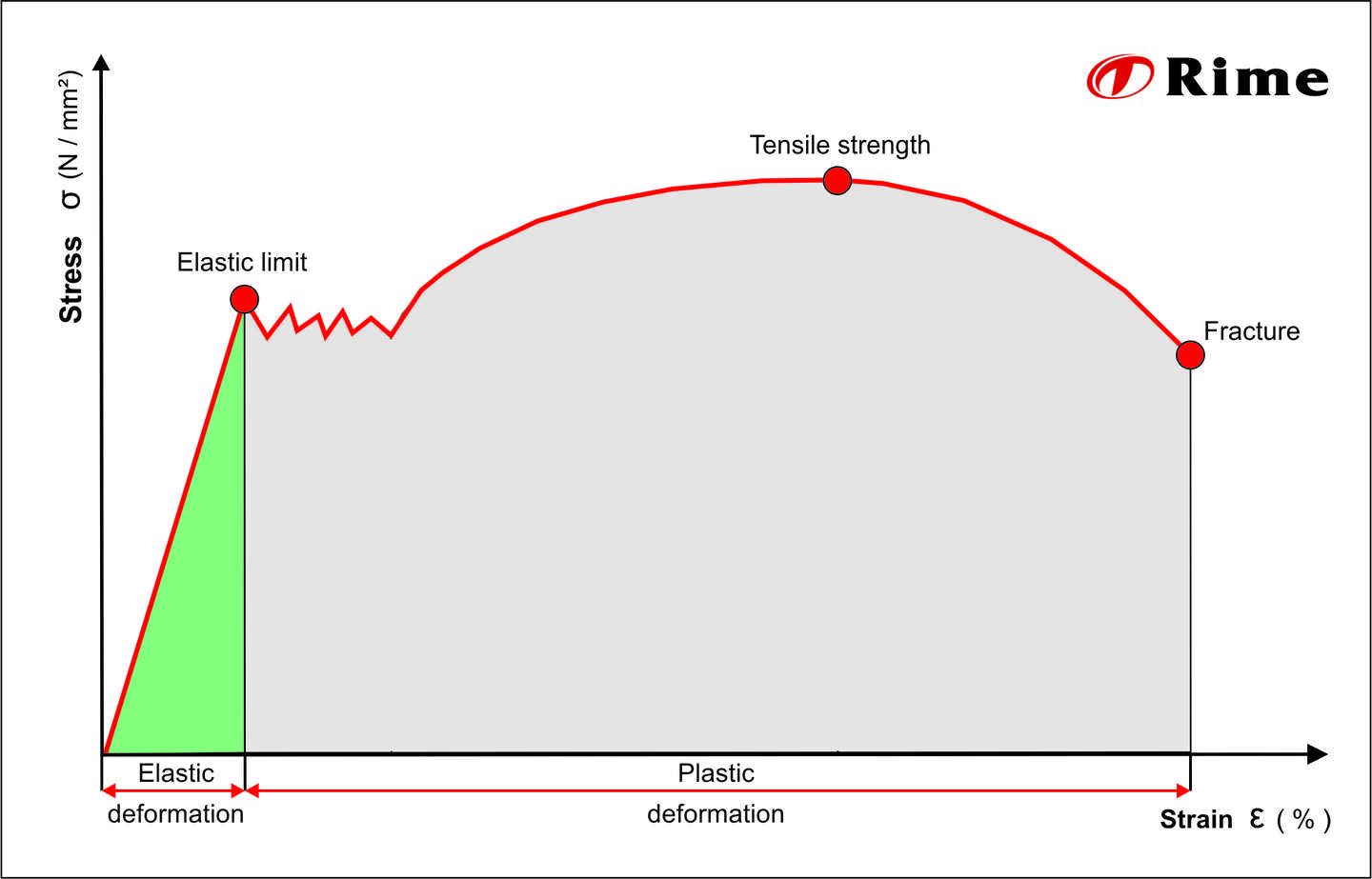


Stress Strain Curve Rime S Wiki
Yield Strength – Yield Point A schematic diagram for the stressstrain curve of low carbon steel at room temperature is shown in the figure There are several stages showing different behaviors, which suggests different mechanical properties To clarify, materials can miss one or more stages shown in the figure, or have totally different stagesStrength is a critical factor in metal uses, for example, some applications require stronger aluminum parts, while some products need high steel hardness or yield strength of steel, this may determine the selection of CNC machining material or product design Here we collect the metal strength chart (tensile, yield strength, hardness, and density included) and mechanical properties chart ofGuide to Fastener Materials Note Steel lowcarbon is generally the default steel selection when no other steel grade is specified, or when no higher grade steel is requiredPlease check your application needs if you are not certain Mechanical Guidelines for Fasteners Screws, Nuts, Bolts, Washers, Pins



Reinforcing Material Charectristic Strength And Types Of Steel Reinforcement


What Is The Difference Between Stress Strain Curve Of High Carbon Steel And Mild Steel Quora
Yield Load(Tons) Ultimate load(Tons) Area of Bar, A=∏ D 2 /4 Yield Strength=Yield Load *24/ Area Tensile Strength = Yield Load*24/ Area 1 ½ in 597 928 0196 in2 Psi 65 Psi 2 ½ in 486 765 0196 in2 Psi 46 Psi 3 ½ in 547 811 0196 in2 Psi 12 Psi 4 ½ in 543 13 0196 in2 Psi 10 Psi 5 1/8 in 705 1095Steel GradesAISI 4340 Chemical information,Mechanical properties Physical properties, Mechanical properties, Heat treatment, and Micro structure Yield Strength 23 σ 02 ≥/MPa Elongation 65 δ5≥ (%) ψ ψ≥ (%) Akv Akv≥/J HBS HRC 30 AISI 4340 Mechanical Properties Tensile strength σb/MPa Yield Strength 154 σ 02 ≥/MPaYield strengths range from 110 ksi through 140 ksi, but we can temper it to other strength levels When compared with standard 4140 heat treated to the same tensile and yield strengths, 4140HW achieves significantly higher toughness, as measured by impact strength (see Figure 9) 4140HW combines medium carbon content with highend chromium,


Tensile Testing


Fce Arcelormittal Com Repository Automotive Product offer Highstrengthsteels Pdf
Yield strength (ksi) 2842 N/A 2535 N/A N/A Ultimate tensile strength (ksi) 4555 N/A 4050 N/A N/A Elongation (% in 2 inches) 36 N/A 3545 N/A N/A Base metal hardness (Rockwell B) 4575 N/A 4568 N/A N/A Cold Rolled Yield strength (ksi) 2540 N/A 29 1729 1525 Ultimate tensile strength (ksi) 3550 N/A 3546 3244 3043 Elongation (% in 2 inches) 2540 N/A 3846 38 40The yield strength of mild steel is 248 megapascal Yield strength is the stress at which a material has undergone an arbitrarily selected amount of deformation, often 02 percent This indicates that when the stress applied on mild steel is 248 megapascal, it shows a measurable amount of deformation, that is, 02 percentThe main purpose of yield strength is to describe and define the stress at which plastic deformation begins in a material, such as mild steelStrength MPa (min) Yield strength (02% offset) MPa (min) Elongation % in 50mm (min) Hardness (max) (Note 2) Austenitic stainless steels Plate Annealed 600 310 40 95 HRB Sheet Annealed 515 5 40 95 HRB or coil 1/4 to full hard 860 1275 515 965 25 9 Wire Annealed 605 max – – – 25mm dia Lightly drawn 660 max and over Bar Cold finished 262 HB Condition A



Steel Material Properties Steelconstruction Info



Stress Strain Diagram Instron
Tensile Strength 58,,000 psi Min Yield Strength 36,000 psi (Over 8" 32,000 psi) Elongation in 2" 23% *For each reduction of 001% below the specified carbon maximum, an increase of 006% manganese above the specified maximum will be permitted up to the maximum of 135% C10 Hot Rolled Plate C1045 Hot Rolled PlateWe can get all parameters to determine the tensile strength of the steel rod from the computer, which is already connected to the machine Tension test on mild steel graph Test Concept Based on the steel specimen's test result, its properties such as yield point, breaking point, and ultimate point data will be plotted as a graphYield Strength ksi 35 55 30 40 30 40 30 40 35 45 55 65 110 185 165 Hardness Brinell Rockwell 150 180 160 180 150 180 150 180 150 0 190 2 3 Conversions For Steel 56 60 65 71 76 81 85 90 95 100 105 110 114 117 1 122 125 128 132 135 138 142 145 149 153 157 162 168 171 176 181 1 194 1 8 215 222


Finding 0 2 Offset Strain Dplot



Tensile Test For 21 Printable And Downloadable Gust
AISI 304 Stainless Steel (UNS S) AISI 304 stainless steel (UNS S) is the most widely used stainless steel, containing 10% Cr and 8105% Ni, and also known as 1 stainless steelType 304 is nonmagnetic under annealing conditions, but after cold working (such as stamping, stretching, bending, rolling), part of the austenite structure may be converted into martensite andDraw a line parallel with the modulus slope with 02% offset, the stress/strength at the intersection with the graphs will be the 02% yield stress/strengthAlloy Steel, quenched and tempered 970 1100 12 Stainless Also called 1 or type 304 stainless steel* N/A 210 Min 450 Typical 500 Min 700 Typical Proof Load An axial tensile load which the product must withstand without evidence of any permanent set Yield Strength The maximum load at which a material exhibits a specific permanent deformation 1MPa = 1N/mm2 = 145 pounds/inch2



Temperature And Strength Of Metals
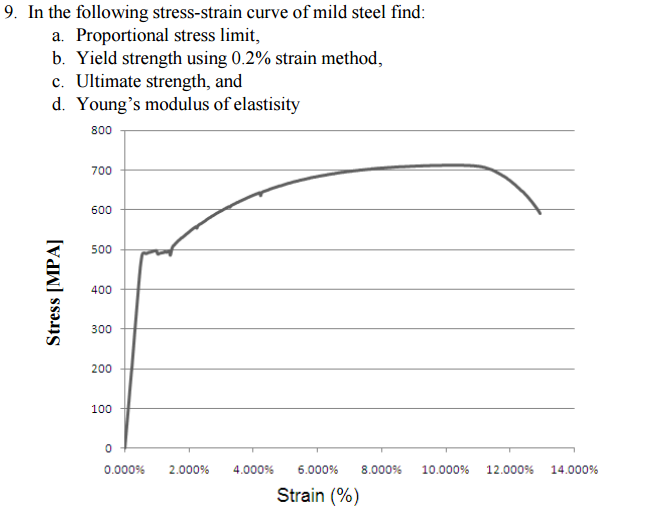


Solved In The Following Stress Strain Curve Of Mild Steel Chegg Com
Ultimate Tensile Strength, psi 63,800 Yield Strength, psi 53,700 Elongation 150% Minimum Properties Rockwell Hardness 1 Iron (Fe) 91 9926% Carbon (C) 018% Manganese (Mn) 06 09% Phosphorus (P) 004% max Chemistry Sulfur (S) 005% max A36 Mild Steel ASTM A36 steel is the most commonly available of the hotrolled steels It is generally available in round rod, squareUltimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength,Yield Strength σ y(MPa) ABS plastics 14 31 40 A53 Seamless and Welded Standard Steel
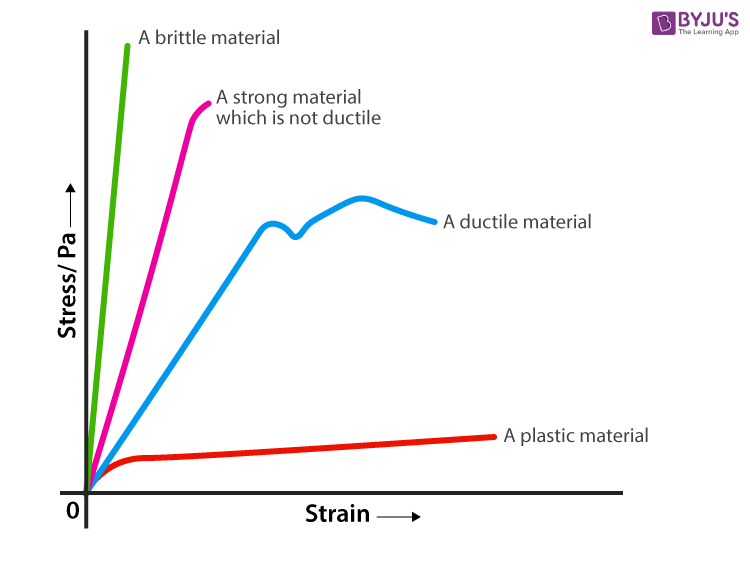


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs



Stress Strain Curve Strength Of Materials Smlease Design
Type ii waste tank flaw ility ysis 1018 steel mechanical property ultimate tensile strength tensile test tec science Chart Showing The Ultimate Tensile Strength And Yield Of Scientific DiagramYield Strength Mechanics Of Materials Ers EdgeNominal Values Of The Yield Strength F Y And Ultimate Tensile TableYield Strength Mechanics Of Materials Ers EdgeHow To Determine The Read More »S275 275 265 255 245 410 400 S355 355 345 335 325 470 450D2 Tool Steel D2 Tool Steel is a versatile highcarbon, highchromium, airhardening tool steel that is characterized by a relatively high attainable hardness and numerous, large, chromiumrich alloy carbides in the microstructure These carbides provide good resistance to wear from sliding contact with other metals and abrasive materials Although other steels with improved toughness or
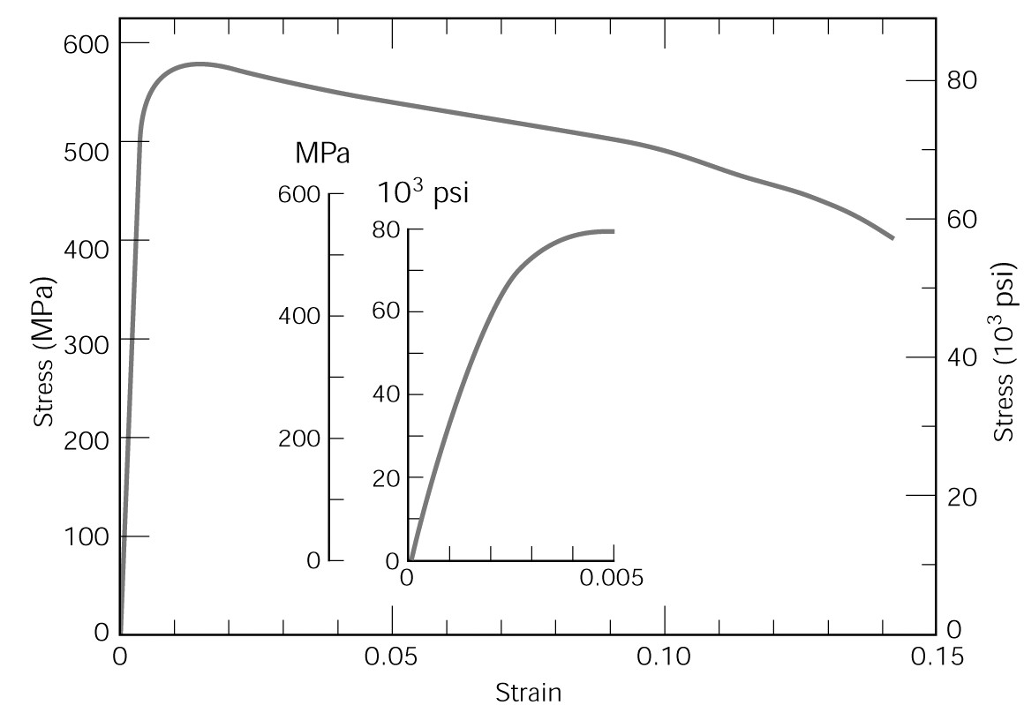


Solved The Following Figure Shows The Tensile Stress Stra Chegg Com
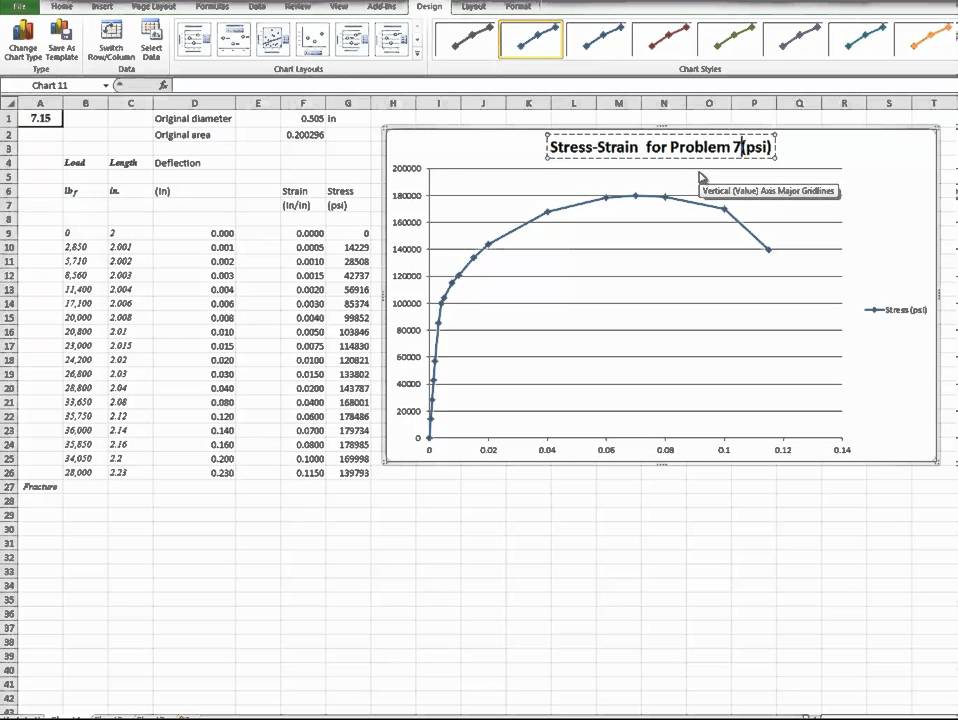


Stress Strain Curve For Steel And Resulting Points Of Interest Youtube
AISI SAE 86 Steel (UNS G860) AISI SAE 86 steel is a commonly used lowalloy material for carburizing, with excellent carburizing response, good hardenability for most section sizes, it has many extensive applications due to its low cost, better machinability, and availabilityIn engineering and materials science, a stress–strain curve for a material gives the relationship between stress and strainIt is obtained by gradually applying load to a test coupon and measuring the deformation, from which the stress and strain can be determined (see tensile testing)These curves reveal many of the properties of a material, such as the Young's modulus, the yield strengthYield Load(Tons) Ultimate load(Tons) Area of Bar, A=∏ D 2 /4 Yield Strength=Yield Load *24/ Area Tensile Strength = Yield Load*24/ Area 1 ½ in 597 928 0196 in2 Psi 65 Psi 2 ½ in 486 765 0196 in2 Psi 46 Psi 3 ½ in 547 811 0196 in2 Psi 12 Psi 4 ½ in 543 13 0196 in2 Psi 10 Psi 5 1/8 in 705 1095



What Is The Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Aluminium And Cast Iron Quora



Engineering Stress Strain Curves For Mild And Stainless Steel Obtained Download Scientific Diagram



Typical Stress Strain Curves For Austenitic Ferritic And Duplex Download Scientific Diagram



Does Unloading Beyond Yield Point Also Affect Tensile Strength Engineering Stack Exchange



Stress Strain



Name Three Mechanical Tests Used To Measure Properties Of Steel Tensile Course Hero



Stress Strain Curve For High Strength Steel Download Scientific Diagram
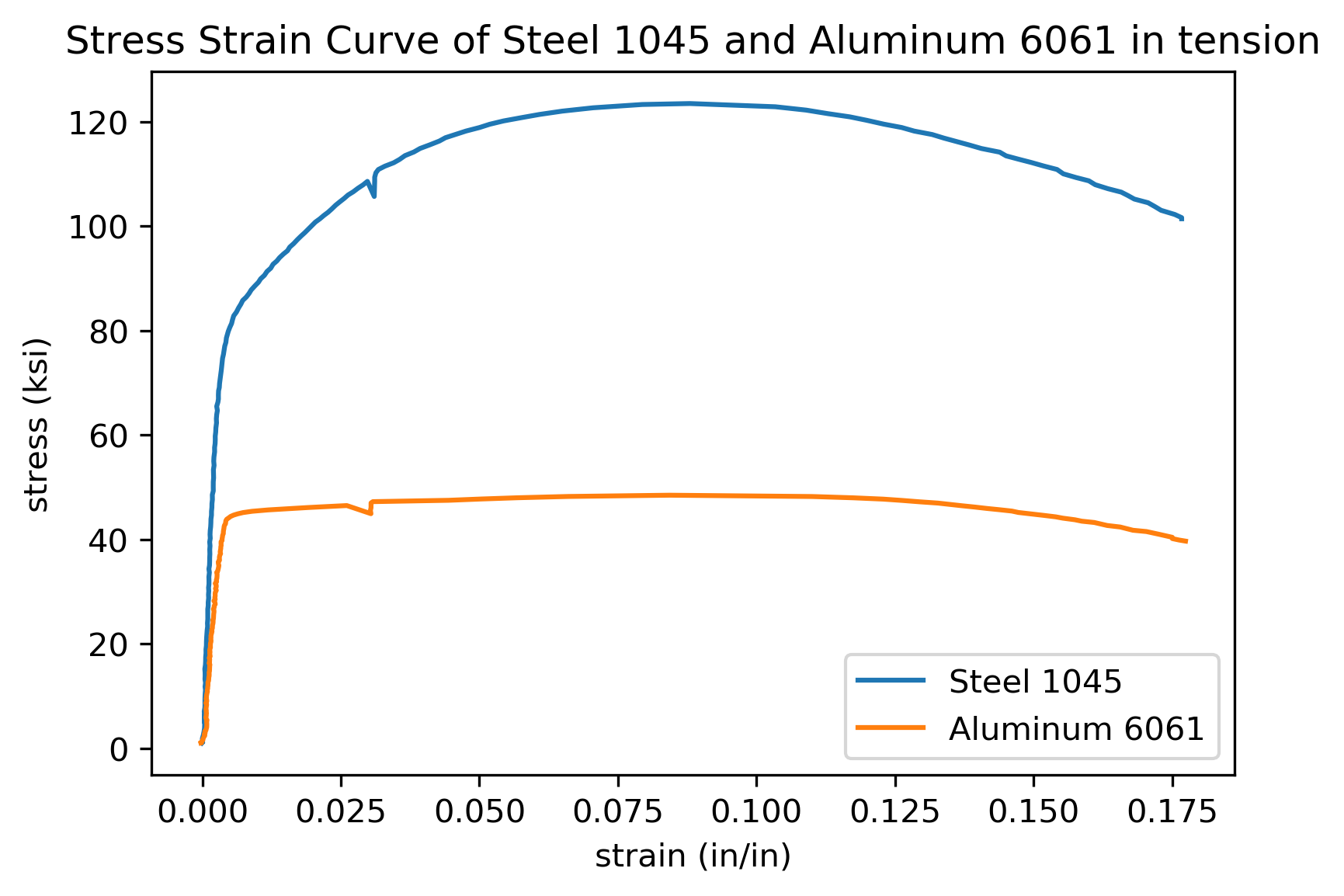


Plotting A Stress Strain Curve With Python And Matplotlib Python For Undergraduate Engineers



Oneclass Figure 6 21 Show The Tensile Engineering Stress Strain Behavior For A Steel Alloy What Is


Q Tbn And9gcqdhkmo7hherjjmwerev9j1zxqfwpmjetj5gvnkildcbtyau41x Usqp Cau
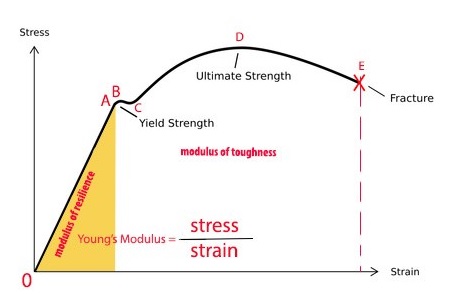


Exploring The Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel The Chicago Curve



Stress Strain Curve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Stress Strain Curve How To Read The Graph
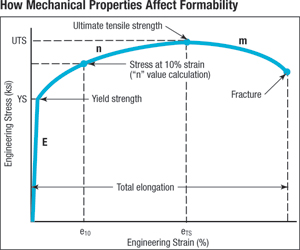


Formability Comparisons Steel And Aluminum Metalforming Magazine Article


Steel Material Properties Steelconstruction Info



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve


What Is The Ultimate Tensile Strength And Yield Strength Of Mild Steel And Hysd Bar Quora
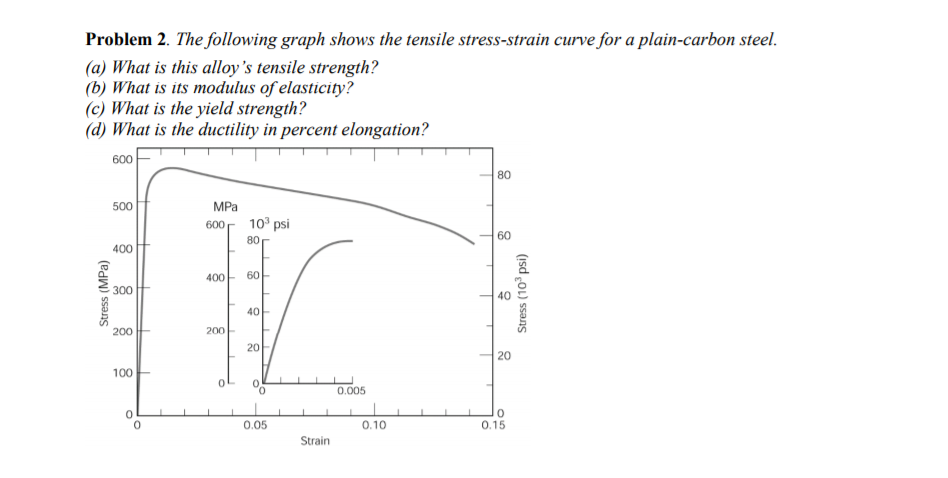


Solved Problem 2 The Following Graph Shows The Tensile S Chegg Com



3 1 4 A Bit More About Tensile Testing
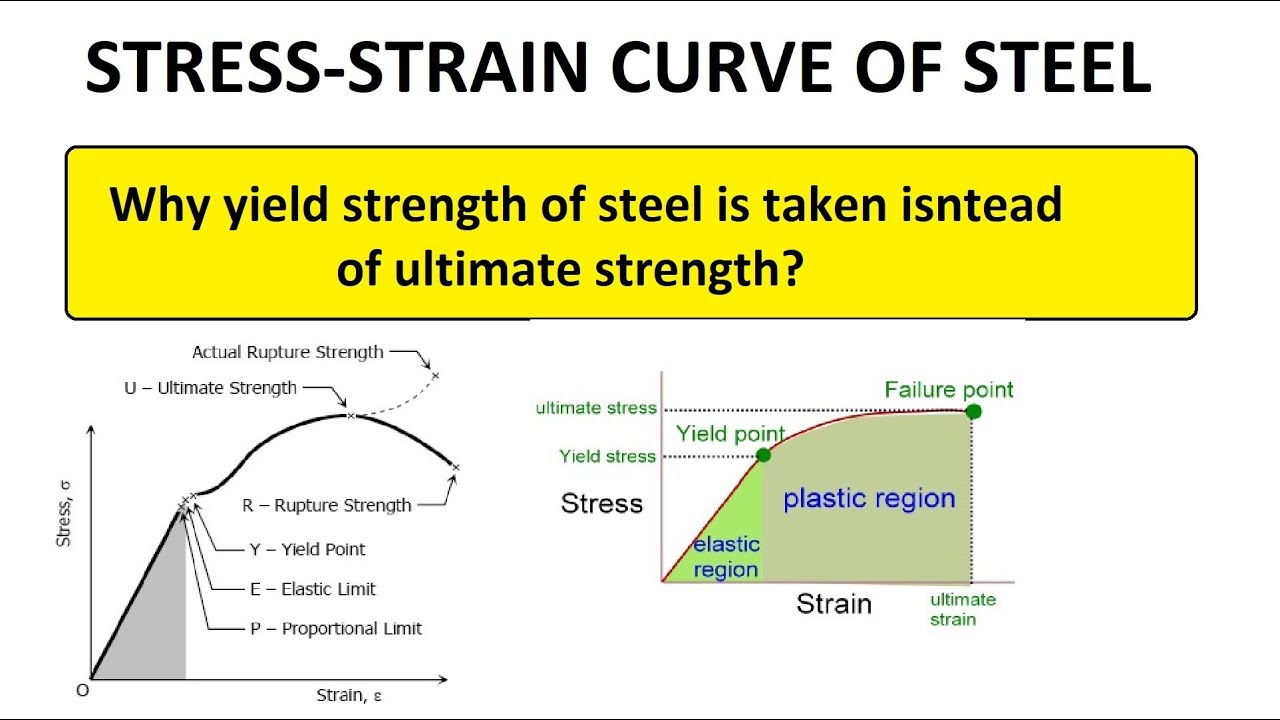


Hindi Stress Strain Curve For Steel Yield Strength Vs Ultimate Strength Youtube



Steel Properties At Low And High Temperatures Total Materia Article
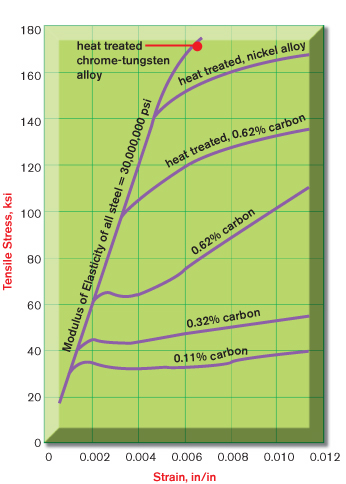


Do Your Materials Measure Up



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv



Cold Formed Steel Wikipedia



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia
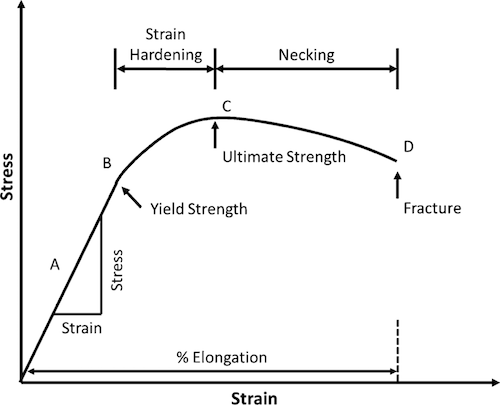


Cee 3710 Strength Versus Stiffness


Engarc L Offset Yield Method
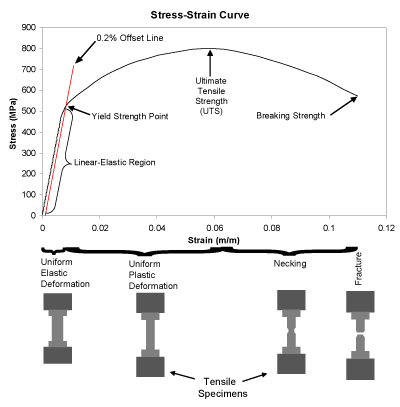


Nondestructive Evaluation Physics Materials
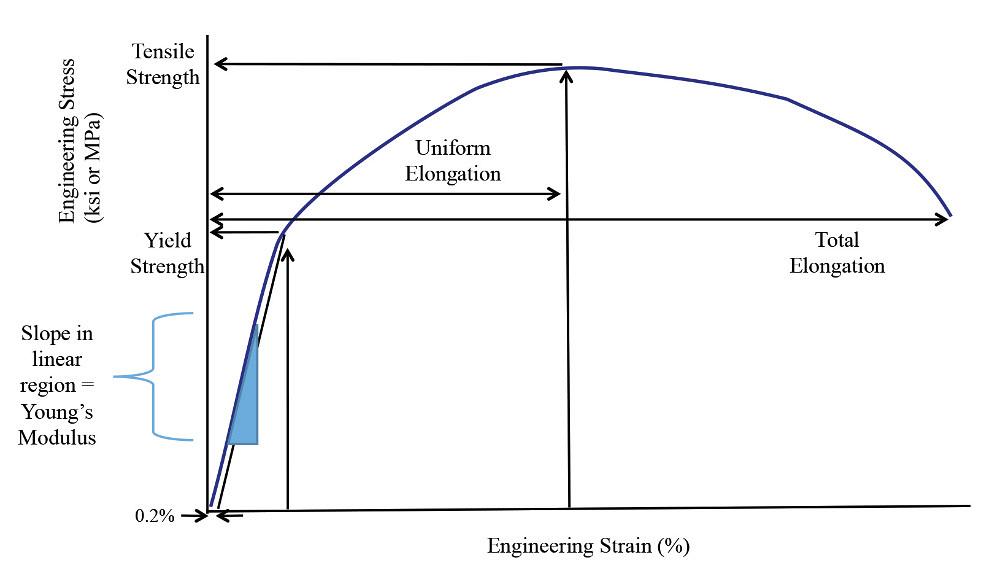


Getting To Know More About The Metal You Are Forming


Q Tbn And9gcsubgeg9vwumror Qhoghyyxdjrgpugf4zei Gvjvgk9mt175y Usqp Cau
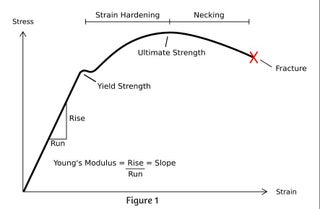


Steps To Analyzing A Material S Properties From Its Stress Strain Curve 9 Steps Instructables



A Tensile Engineering Stress Strain Curves Of Aisi 4340 Steel Tempered Download Scientific Diagram



Virtual Labs



Stress Strain Curve For Steel Bars Figure 6 Represents Bilinear Download Scientific Diagram



Yield Strength



Why Does The Stress Strain Curve Decrease Engineering Stack Exchange
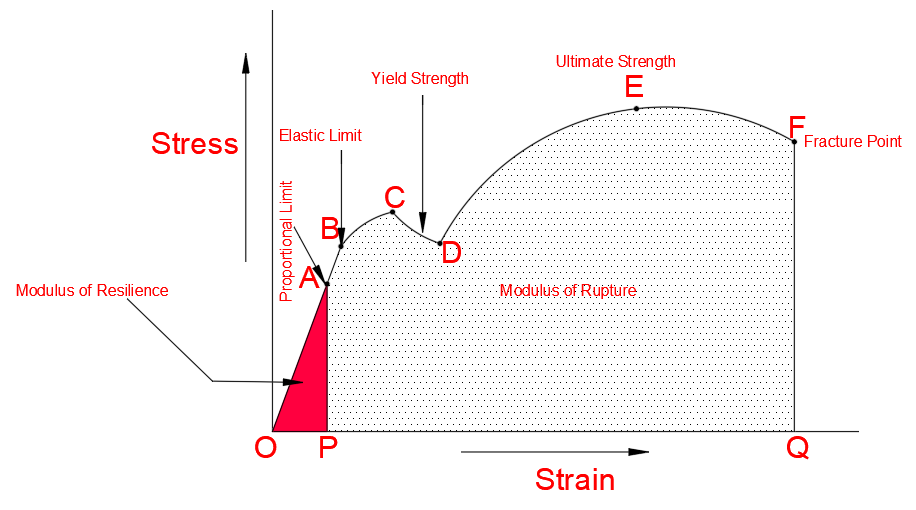


Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Explained Civilmint


Influence Of Temperature On Mechanical Properties Fracture Morphology And Strain Hardening Behavior Of A 304 Stainless Steel


Stress Strain Curve Explanation Stages Mild Steel Engineering Intro



Steel Properties At Low And High Temperatures Total Materia Article



Stress Strain Data 4130 Steel Evocd
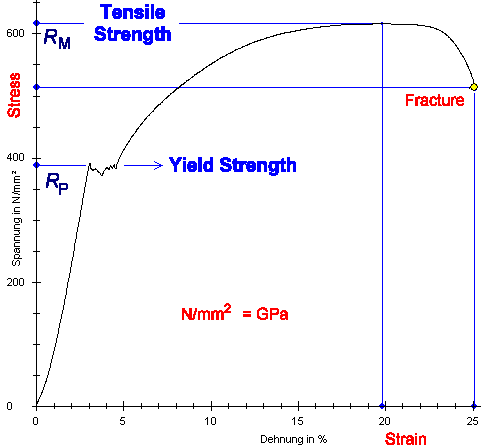


Science Of Uniaxial Deformation


Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau



Question Regarding Ultimate Limit State Design Structural Engineering General Discussion Eng Tips



Sheet Metal Tension Testing Admet



Minimum Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
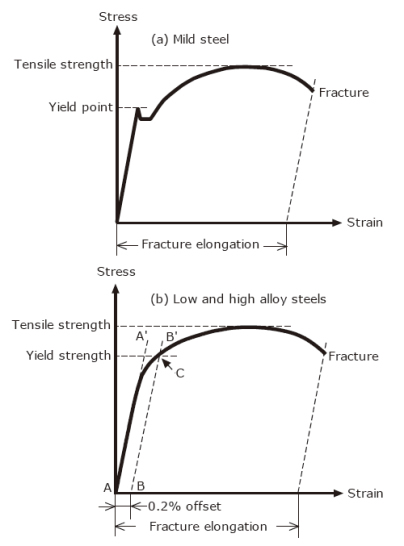


The Abc S Of Arc Welding Education Center Kobelco Kobe Steel Ltd
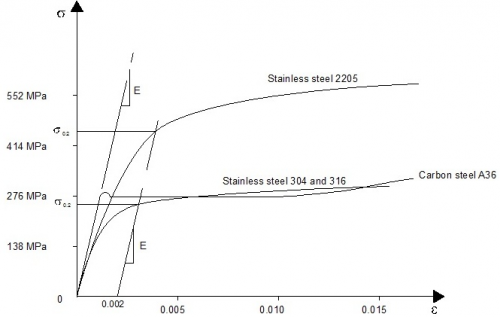


Steel Material Properties Steelconstruction Info



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia



Tensile Test Experiment Materials Science And Engineering Michigan Technological University


Tensile Testing
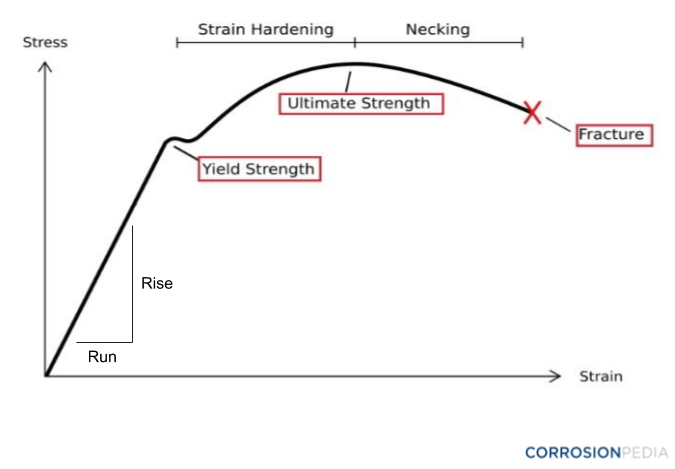


What Is A Proof Stress Definition From Corrosionpedia



Tensile Test Experiment Materials Science And Engineering Michigan Technological University


Q Tbn And9gctkrzf52tulw Hck4iec8kqmmvrheff2kzrugh6dmtmgku6pybl Usqp Cau



Comparison Of Stress Strain Curves For Stainless Steel And Carbon Steel Download Scientific Diagram
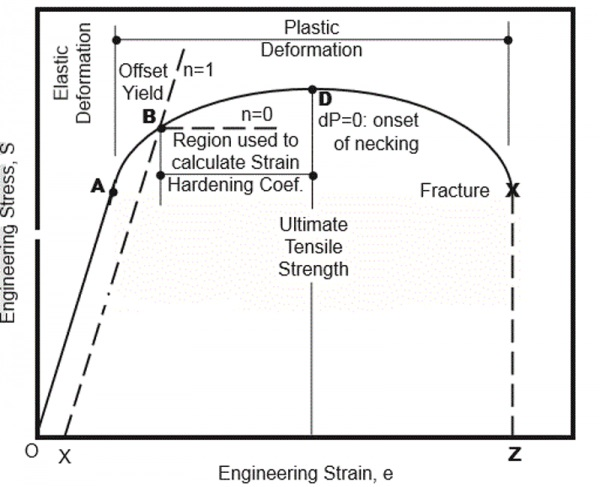


Which Methods To Use For Sheet Metal Tension Testing



How Come The Yield Strength Is Greater Than Tensile Strength When Testing A Steel Specimen Quora
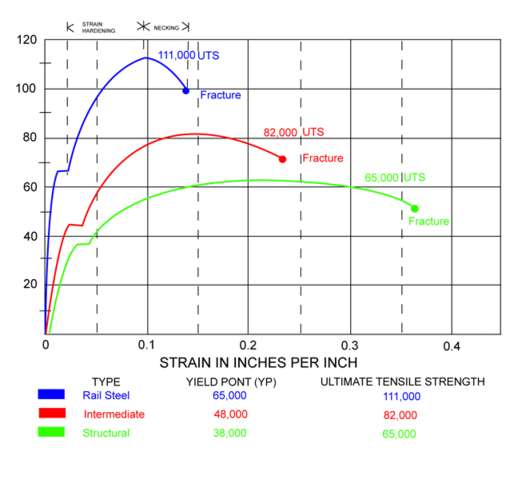


Chemical Mechanical Properties Of Rail Steel Angles Jersey Shore Steel



How To Measure Tensile Strength Elastic Modulus And Ductility Rolled Alloys Inc
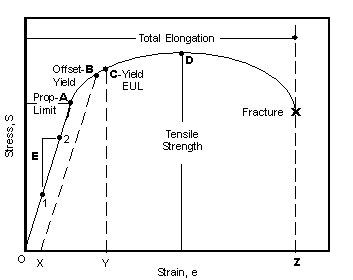


Astm E8 Measuring The Tensile Strength Of Metals



A Comparative Stress Strain Relationships Of Low Carbon Steel And Download Scientific Diagram



The Following Figure Shows The Tensile Stress Strain Curve For A Plain Carbon Steel A What Is This Alloy S Tensile Strength B What Is Its Modulus Of Elasticity C What Is The Yield Strength


Influence Of Temperature On Mechanical Properties Fracture Morphology And Strain Hardening Behavior Of A 304 Stainless Steel
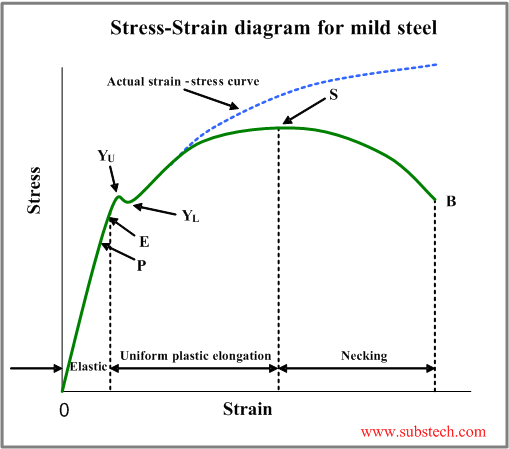


Tensile Test And Stress Strain Diagram Substech


Why Do We Use 0 2 Offset In Aluminum Stress Strain Curve Quora



Mechanical Properties Of 4140 Steel Evocd



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
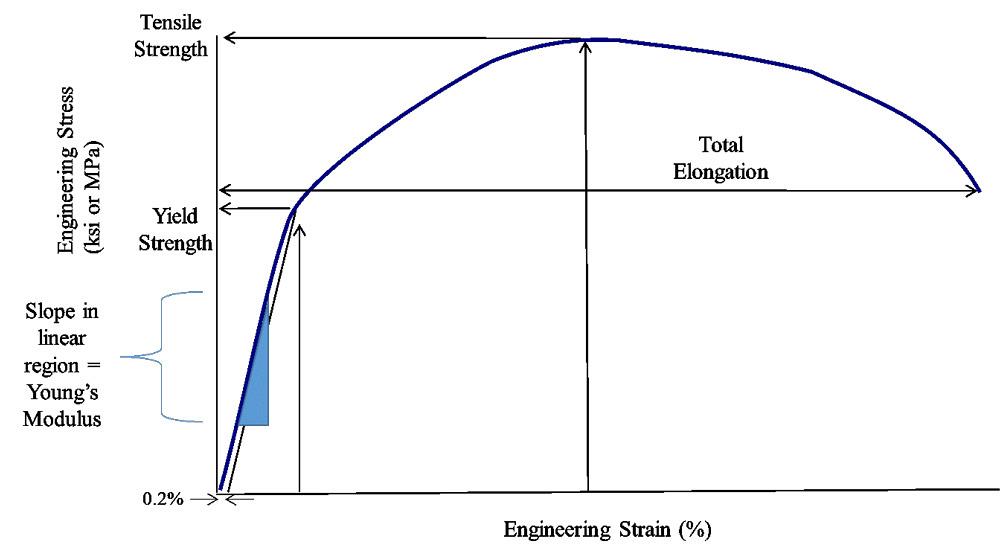


The Differences Between Stiffness And Strength In Metal



6 Tensile Stress Strain Curve For Steel A Elastic Limit B Upper Download Scientific Diagram


Yield Engineering Wikipedia



Mechanical Properties Of Austenitic Stainless Steel 304l And 316l At Elevated Temperatures Sciencedirect



Chapter 26 Biomechanics Musculoskeletal Key



Structural Material Wikipedia



Stress And Strain Diagram For Steel Wiring Diagram Portal
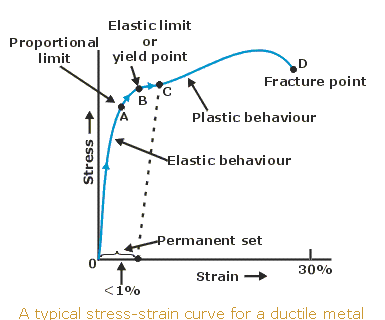


Steps To Analyzing A Material S Properties From Its Stress Strain Curve 9 Steps Instructables


5 Grades 60 And 80 Stress Strain Curves For Astm A615 And 06 Download Scientific Diagram



Virtual Labs



Steel Properties At Low And High Temperatures Total Materia Article




コメント
コメントを投稿